Source for the North
www.fishweb.com
MICHIGAN FISHING
Fishing Thermocline
|
Michigan Fishing Tips Fishing Thermocline
|
|
Locating feeding fish is one of the most important skills a fisherman can
develop. You can mark fish on your fish finder and not entice them to strike
your lure if they are not in their "feeding zone"!
Most species of fish have a preffered temperature of water that they
will actively feed in. Find this area of temperture with fish present and
you will greatly increase your chances of catching fish. Remember, fish are
cold blooded. In water too cold, fish will be dormant, sluggish and will
not feed. In water too warm, they will be seeking a more comfortable
environment. So, an understanding of how different temperatures
of water break up will help.
|
Here are two main ways temperatures of water will break up:
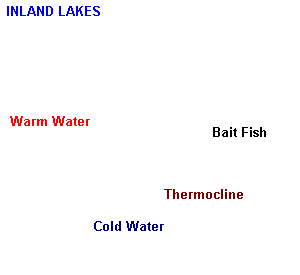
On inland lakes, water temperatures tend to settle into horizonal layers of
warm water and cold water that are seperated by a moderating layer known as
the "thermocline". The thermocline will be the most active "feeding zone".
On larger bodies of water like the oceans and Great Lakes, masses of water
temperature are much larger and in a constant state of change. The location of
these large masses of temperature are highly affected by the changes in
weather conditions. These large masses of warm and cold water also have
a moderating layer that is known as a "temperature break". Because of the
constant shifting of the warm and cold masses temperture breaks often appear
as a vertical layer. The area of, and immediately around, the temperature
break is the most active "feeding zone".
|
|
M.I. Advertisement Pricing
|